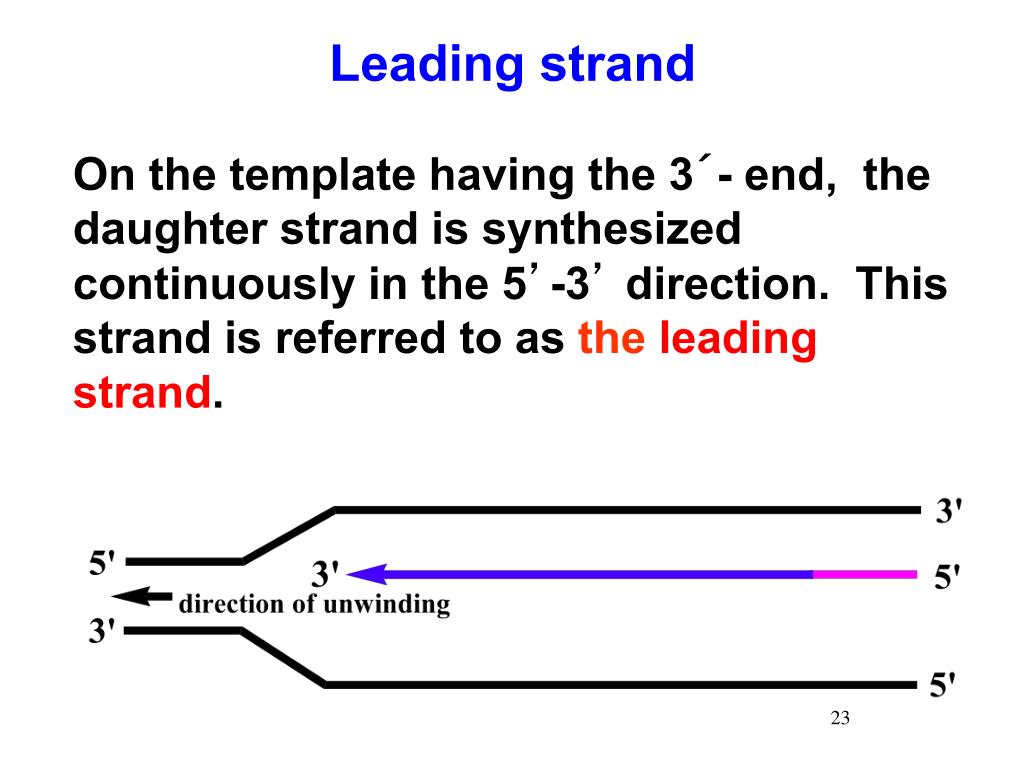
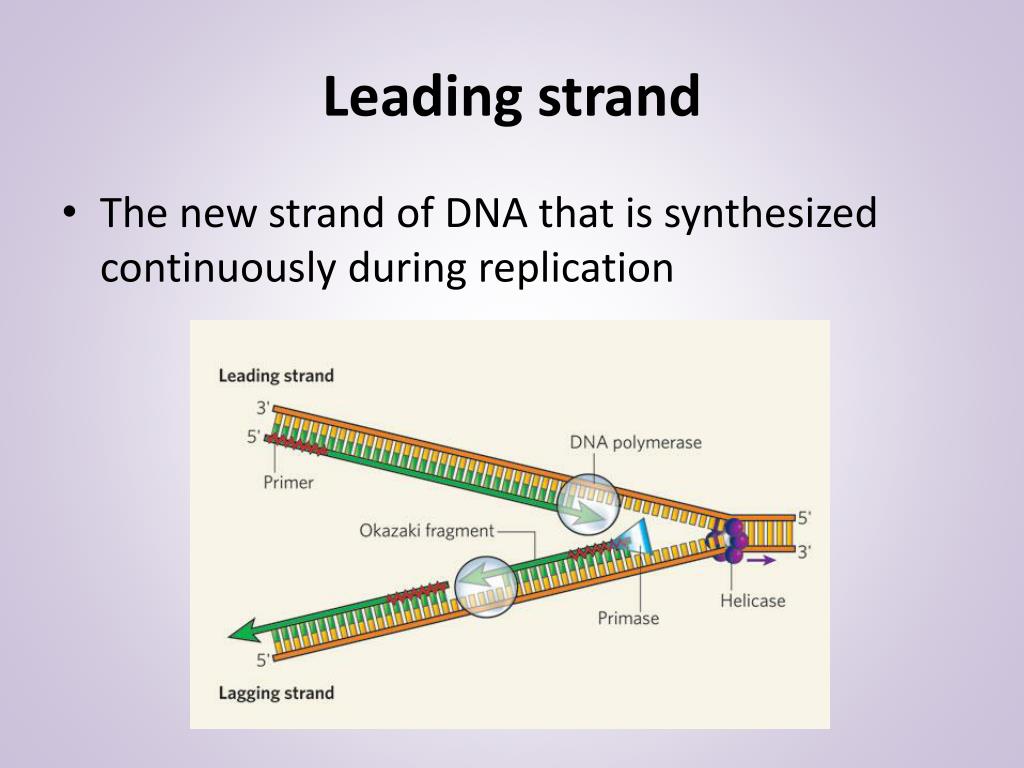
Template Strand Definition Biology
Template Strand Definition Biology - (2) in dna replication each strand of the duplex acts as a template. Web each strand of dna acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell. Transcription is the process of copying a segment of dna into rna. Which is one of strand in the dna that is present after they are being unwounded by the enzyme. Web other articles where template replication is discussed: This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web dna replication is semiconservative, meaning that each strand in the dna double helix acts as a template for the synthesis of a new, complementary strand. Molecular replication:.the process is called a template replication—one strand serves as the mold for the. Web biology glossary search by everythingbio.com.
Dna Template Strand shatterlion.info
The enzyme binds to a special rna molecule that contains a sequence complementary to the telomeric repeat. The other strand, the coding. Transcription machinery interacts with the template strand to produce an mrna. Web other articles where template replication is discussed: A template strand is the term that refers to the strand used by dna polymerase or rna polymerase to.
biochemistry DNA base pair heading Biology Stack Exchange
Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. This process takes us from one starting molecule to two daughter molecules, with each newly formed. Less than 2% of the human genome can be tran… Web one strand of dna is called the coding strand and the other is the template strand. (1) a pattern serving as a mechanical guide.
Simple Lagging Strand Definition Idea In 2022 Typography Art Ideas
Web the strand of dna from which mrna is formed after transcription is known as the template strand or the antisense strand. A template strand is the term that refers to the strand used by dna polymerase or rna polymerase to attach complementary bases during dna. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary.
Overview of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Template DNA strands
Which is one of strand in the dna that is present after they are being unwounded by the enzyme. Web each strand of dna acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. Dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. (2) in dna replication each strand of the duplex acts as a template. The segments of.
Answered Template strand New strand New strand… bartleby
Web noun (genetics) the noncoding strand of a dna molecule that is used as a template for rna synthesis. The other strand, the coding. The template strand is usually. (2) in dna replication each strand of the duplex acts as a template. (1) a pattern serving as a mechanical guide.
PPT DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3371102
Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell. Overview of template strand the rna and the dna are made of. Transcription machinery interacts with the template strand to produce an mrna. Dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. Replication produces two identical dna double helices, each with one new and one old strand.
Telomeres and daughter strands Biology Stack Exchange
The segments of dna transcribed into rna molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger rna (mrna). Web noun (genetics) the noncoding strand of a dna molecule that is used as a template for rna synthesis. Overview of template strand the rna and the dna are made of. Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used.
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein. Overview The
Web by convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. Transcription machinery interacts with the template strand to produce an mrna. Web biology glossary search by everythingbio.com. (1) a pattern serving as a mechanical guide.
Image result for template strand Transcription, Study biology
Web other articles where template replication is discussed: The antisense strand is referred to as the. Web each strand of dna acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. A template strand is the term that refers to the strand used by dna polymerase or rna polymerase to attach complementary bases during dna. Transcription is the process.
PPT DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6899779
Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. (1) a pattern serving as a mechanical guide. Web noun (genetics) the noncoding strand of a.
Web the strand of dna from which mrna is formed after transcription is known as the template strand or the antisense strand. A template strand is the term that refers to the strand used by dna polymerase or rna polymerase to attach complementary bases during dna. Web the coding strand is the dna strand that encodes codons and whose sequence corresponds to the mrna transcript produced. Dna replication occurs through the help of several enzymes. (1) a pattern serving as a mechanical guide. Web the strand of dna which is like the template from which the mrna is made is known as the template strand. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell. The other strand, the coding. Web one strand of dna is called the coding strand and the other is the template strand. Web dna replication is semiconservative, meaning that each strand in the dna double helix acts as a template for the synthesis of a new, complementary strand. The segments of dna transcribed into rna molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger rna (mrna). Transcription machinery interacts with the template strand to produce an mrna. Overview of template strand the rna and the dna are made of. Web other articles where template replication is discussed: Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed. This process takes us from one starting molecule to two daughter molecules, with each newly formed. Web in transcription, a region of dna opens up. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. The template strand is usually.
Molecular Replication:.the Process Is Called A Template Replication—One Strand Serves As The Mold For The.
The template strand is usually. This process takes us from one starting molecule to two daughter molecules, with each newly formed. The segments of dna transcribed into rna molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger rna (mrna). Web the strand of dna which is like the template from which the mrna is made is known as the template strand.
Dna Replication Occurs Through The Help Of Several Enzymes.
Overview of template strand the rna and the dna are made of. (2) in dna replication each strand of the duplex acts as a template. Web the coding strand is the dna strand that encodes codons and whose sequence corresponds to the mrna transcript produced. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell.
Web One Strand Of Dna Is Called The Coding Strand And The Other Is The Template Strand.
Web dna replication is semiconservative, meaning that each strand in the dna double helix acts as a template for the synthesis of a new, complementary strand. (1) a pattern serving as a mechanical guide. Transcription machinery interacts with the template strand to produce an mrna. This template strand is called the noncoding strand.
The Antisense Strand Is Referred To As The.
Web noun (genetics) the noncoding strand of a dna molecule that is used as a template for rna synthesis. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. One strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Replication produces two identical dna double helices, each with one new and one old strand.