Non Template Dna Strand
Non Template Dna Strand - Fine lines are dna regions; +1 corresponds to the start site of. Web one strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. The copy of the template strand is read by ribosomes, which then produce a. In most organisms, the strand of dna that serves as the. Dashed lines are rna regions; The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. The new strand of dna produced by this mechanism is termed the lagging strand. Web the term template strand refers to the dna sequence that can duplicate itself during mrna synthesis.
Gene Expression Transcription Agriculture, and Biotechnology
During initiation, σ subunit interactions with the nontemplate dna regulate promoter complex formation and lifetime, abortive synthesis, and start site. Dashed lines are rna regions; Medical schools in times of war: The new strand of dna produced by this mechanism is termed the lagging strand. Rather, they require an rna primer, which is a short piece of rna base paired.
Participation of the nontemplate DNA strand in HQ formation detected
Web one strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Web the term template strand refers to the dna sequence that can duplicate itself during mrna synthesis. Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. Transcription.
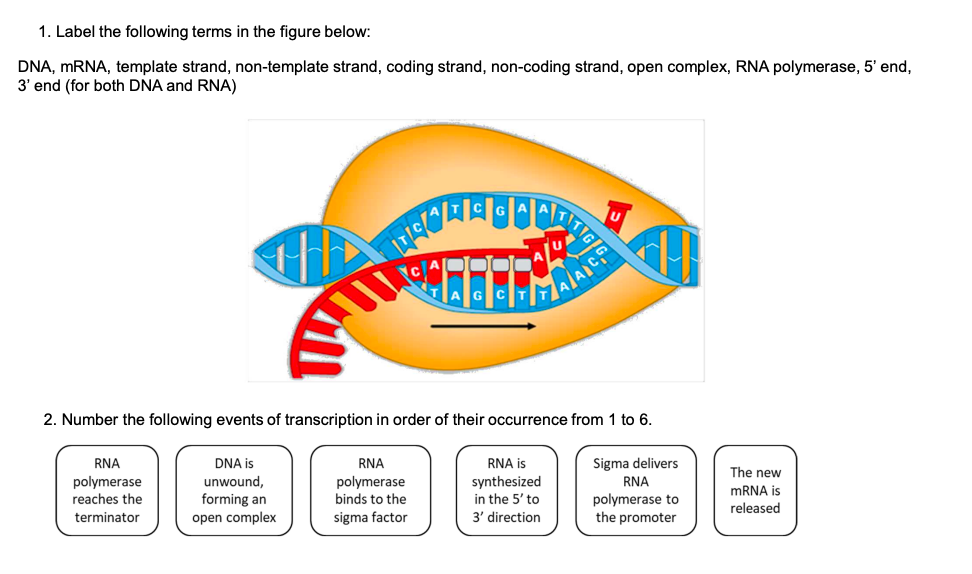
Solved 1. Label the following terms in the figure below
By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. Difference between coding strand and template strand visit byju’s biology for more interesting topics. Frequently asked questions q1 what is mrna? These enzymes utilize energy from atp to move on dna, destabilize the hydrogen bonds between bases, and separate the two strands of the double helix..
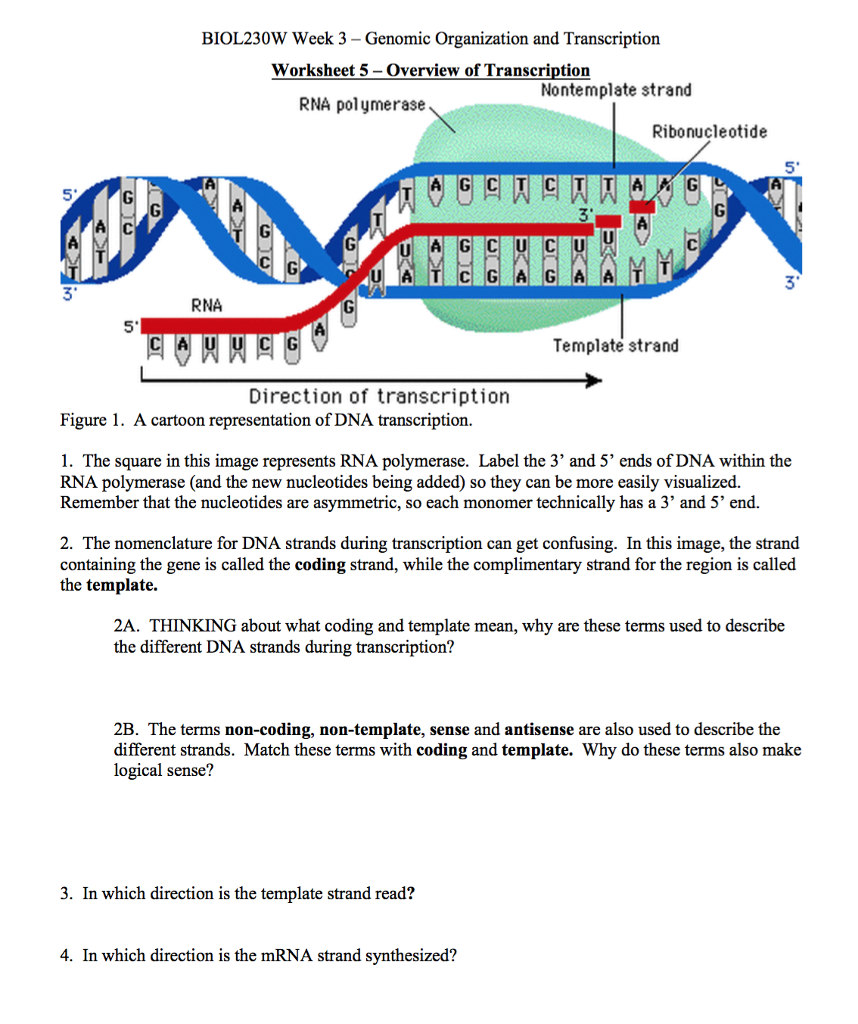
Solved Part A (3 points) Nontemplate strand of DNA Template
These enzymes utilize energy from atp to move on dna, destabilize the hydrogen bonds between bases, and separate the two strands of the double helix. By convention, the coding strand is the strand used when displaying a dna sequence. Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of.
Coding Strand of DNA bartleby
The copy of the template strand is read by ribosomes, which then produce a. Web the term template strand refers to the dna sequence that can duplicate itself during mrna synthesis. In most organisms, the strand of dna that serves as the. Your article has been reviewed by three peer reviewers, and the evaluation has been overseen by a reviewing.
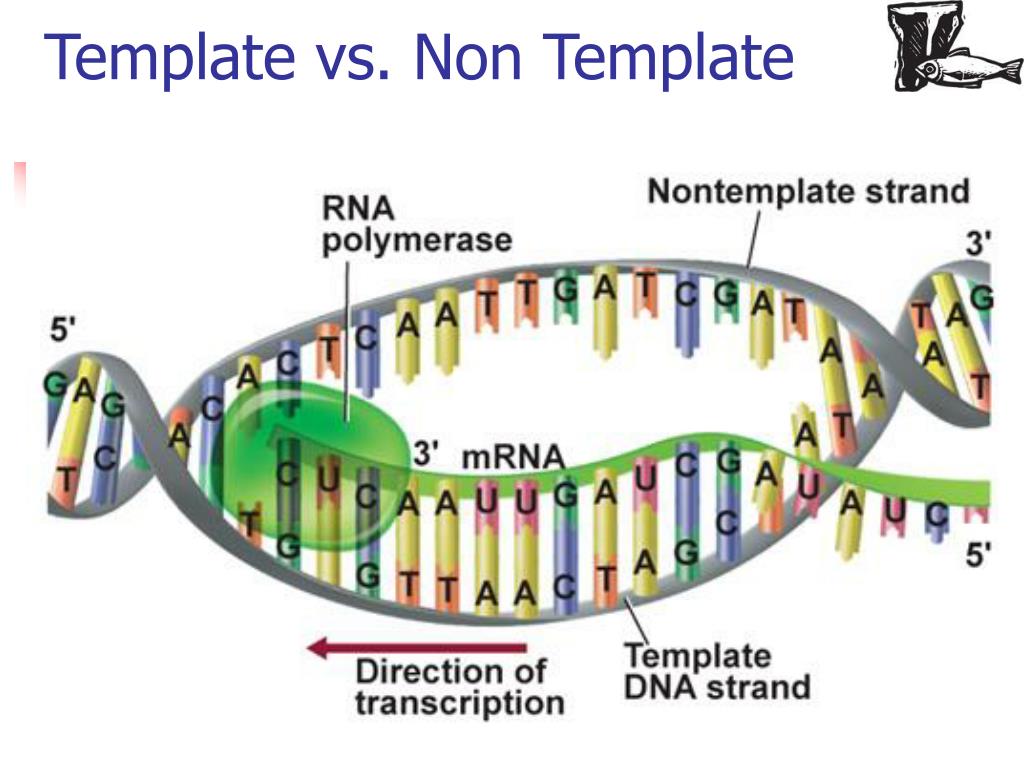
Non Template Strand
Rather, they require an rna primer, which is a short piece of rna base paired to the dna template, thereby Web one strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Dashed lines are rna regions; Web the term template strand refers to the dna sequence that can duplicate itself during mrna synthesis. Web.
Non Template Strand
However, some dna polymerases can synthesize dna across two discontinuous templates by binding and juxtaposing them, resulting in synthesis across the junction. This is the strand that is used by convention when presenting a. Web oligonucleotides used as templates in the transcription assays. Transcription is the first step in gene expression. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction.
Template DNA base pairing with the nontemplate DNA base at the10th
This is the strand that is used by convention when presenting a. Web one strand, the template strand, serves as a template for synthesis of a complementary rna transcript. Web despite possessing a short promoter consensus element, the ar9 nvrnap holoenzyme protects an extensive region of dna flanking the tss (position −35 to +20 in the template strand and positions..
The coding strand of DNA is 5'AATTCAAATTAGG3'
Mrna may be anything between 100 and thousands of nucleotides long. This is the strand that is used by convention when presenting a. +1 corresponds to the start site of. These enzymes utilize energy from atp to move on dna, destabilize the hydrogen bonds between bases, and separate the two strands of the double helix. Web oligonucleotides used as templates.
Non Template Strand
+1 corresponds to the start site of. The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases. Frequently asked questions q1 what is mrna? Web ap®︎/college biology > gene expression and regulation > transcription and rna processing overview of transcription google classroom in.
Fine lines are dna regions; Dna polymerases use an uninterrupted template strand to direct synthesis of dna. Rather, they require an rna primer, which is a short piece of rna base paired to the dna template, thereby In a cell, antisense dna serves as the template for producing messenger rna (mrna), which directs the synthesis of a protein. During dna replication, the template is generated by enzymes known as helicases. It is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. In most organisms, the strand of dna that serves as the. The new strand of dna produced by this mechanism is termed the lagging strand. Medical schools in times of war: However, some dna polymerases can synthesize dna across two discontinuous templates by binding and juxtaposing them, resulting in synthesis across the junction. Web the term template strand refers to the dna sequence that can duplicate itself during mrna synthesis. Mrna may be anything between 100 and thousands of nucleotides long. This is the strand that is used by convention when presenting a. Web codons are a sequence of triplets found in the transcribed mrna strand. Frequently asked questions q1 what is mrna? +1 corresponds to the start site of. Web ap®︎/college biology > gene expression and regulation > transcription and rna processing overview of transcription google classroom in transcription, the dna sequence of a gene is transcribed (copied out) to make an rna molecule. Dashed lines are rna regions; Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. The copy of the template strand is read by ribosomes, which then produce a.
However, Some Dna Polymerases Can Synthesize Dna Across Two Discontinuous Templates By Binding And Juxtaposing Them, Resulting In Synthesis Across The Junction.
The new strand of dna produced by this mechanism is termed the lagging strand. Your article has been reviewed by three peer reviewers, and the evaluation has been overseen by a reviewing editor and gisela storz as the. Medical schools in times of war: The other strand, the coding strand, is identical to the rna transcript in sequence, except that it has uracil (u) bases in place of thymine (t) bases.
In Most Organisms, The Strand Of Dna That Serves As The Template For One Gene May Be The Nontemplate Strand For Other Genes Within The Same Chromosome.
During dna replication, the template is generated by enzymes known as helicases. Dna polymerases use an uninterrupted template strand to direct synthesis of dna. These enzymes utilize energy from atp to move on dna, destabilize the hydrogen bonds between bases, and separate the two strands of the double helix. In most organisms, the strand of dna that serves as the.
Fine Lines Are Dna Regions;
Web despite possessing a short promoter consensus element, the ar9 nvrnap holoenzyme protects an extensive region of dna flanking the tss (position −35 to +20 in the template strand and positions. +1 corresponds to the start site of. During initiation, σ subunit interactions with the nontemplate dna regulate promoter complex formation and lifetime, abortive synthesis, and start site. Web oligonucleotides used as templates in the transcription assays.
Web Codons Are A Sequence Of Triplets Found In The Transcribed Mrna Strand.
Difference between coding strand and template strand visit byju’s biology for more interesting topics. This is the strand that is used by convention when presenting a. Here we show that when. Mrna may be anything between 100 and thousands of nucleotides long.